
Natural Vitamins for parrot: Their name is a derivative of Latin (Vita: life) and -amine.
Organic substances are essential for the growth and proper functioning of an organism that cannot synthesize it itself. (Petit Larousse).
Fat-soluble vitamins
Danger: an overdose of these vitamins can have severe consequences (poisoning) for our parrots. Unlike water-soluble vitamins, which are rapidly eliminated from body fluids, fat-soluble vitamins are stored in the liver of birds.
Vitamin A
Vitamin A comes in two forms:
1. Retinol or Retinal
It is found in animal fats and fish oil. The animal liver has a very high level of vitamin A, but you should not give it to your parrot more than once a month because of the toxic substances it contains. Retinol is also found in dairy products.
2. Provitamin A (carotene)
Beta-carotene is the most active form of carotene and is converted into vitamin A by enzymatic actions in the mucous membranes of the intestine and the liver. It is the best source of vitamin A for parrots. It is found in orange or red fruits and vegetables as well as in vegetables with dark green foliage. The advantage of beta carotene is that you cannot give your bird too much (no risk of poisoning) unlike vitamin supplements sold on the market, including feed.
The seeds are known to be very low in vitamin A (as well as corn, potatoes, grapes, lettuce, bananas, and apples). A diet consisting only of seeds can seriously jeopardize the health of your bird.
Vitamin A is easily oxidized, we must pay attention to the treatment of food that we give to his parrot.
Hypovitaminosis A (vitamin A deficiency) is a common disease in psittacines that veterinarians often encounter, yet one of the easiest to prevent.
Deficiency in parrots
Soft eggs, difficulty in reproduction, stunted growth, deformity of bones, dry and rough skin, more than dull plumage, discharge from eyes and nose, chronic sinusitis, little or no resistance to infections, accentuates bad night vision, visual disturbances, friable beak, diseases of the respiratory, digestive and reproductive systems.
Parrot Vitamins

Vitamin A
Symptoms
One or more of these symptoms: sneezing, loud breathing, runny nose, stuffy or crusted nostril, lethargy, diarrhea, tail swing (up and down), thinness, dull plumage (glow and color), discharge from the eyes, lack appetite, bad breath.
Overdose
(Hypervitaminosis A). Just as a lack of vitamin A can be harmful to the bird, an overdose will be just as damaging. Many feeds on the market are over-vitamin and can cause serious problems for parrots. It is not recommended to offer vitamin supplements to parrots consuming feed. Overdose can lead to kidney gout.
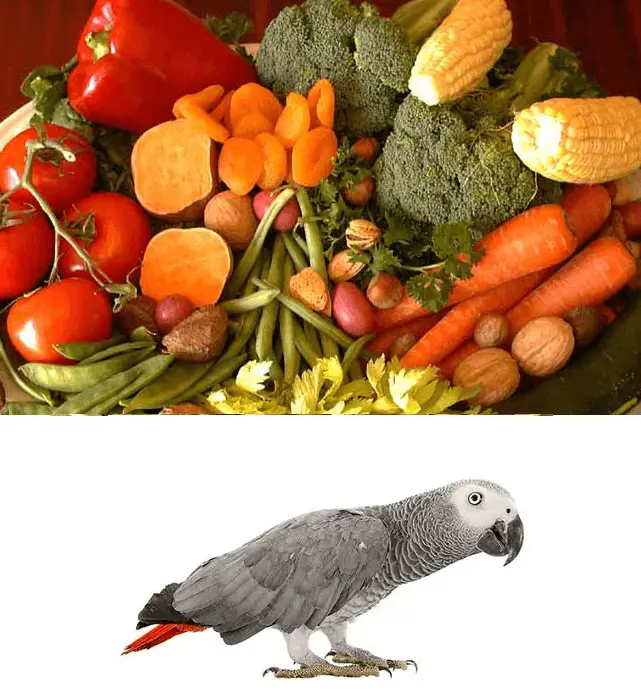
Vitamin A is found in
Fresh red peppers * 21,000
Dried red peppers * 16.00
Beef liver 45,000
Broccoli leaves 77,000 Broccoli
flowers 3,000
Dried apricots 16,000
Dandelions 14,000
Carrots and carrot juice 10,000
Sweet potatoes (“sweet”) 9,000
Spinach 8,800
Turnips 7,600
Mangoes 4,100
Leaves Endive 3,300
Egg yolk 3,000
Cantaloupe 4,000
Papayas 2,000
Butter 3,500
* International unit / 100 g.
Other foods containing beta-carotene: winter and summer squash, pumpkins, peaches, watermelons, spirulina, parsley, red tomatoes, unrefined palm oil, beets, jalapenos, sweet red peppers, fruits of passion, escarole, green peas, asparagus, nectarines, plums, cherries, kiwis, strawberries, etc.
* IU International unit of measurement used to express the biological activity of vitamins.
* Parrots do not salivate. They, therefore, do not detect the hot side of red peppers like humans.
Vitamin D
Calciferol
When we talk about vitamin D, we are generally referring to two chemical compounds:
- Vitamin D2: ergocalciferol
- Vitamin D3: cholecalciferol
These two vitamins have much the same effect in humans, but vitamin D3, (cholecalciferol) is up to 100 times more effective for parrots and is present mainly in products of animal origin (fish in particular) and by the action of the sun’s ultraviolet rays or artificial UV rays from fluorescent tubes (full spectrum). These convert the precursors of vitamin D into vitamin D3 in the skin of the bird.
Some plant sources contain vitamin D in the form of ergocalciferol or vitamin D2. Mammals can use this particular form of vitamin D, but avian species, unfortunately, cannot.
This vitamin is relatively heated stable but degrades rapidly under the action of light, oxygen, and acids.
Unlike other fat-soluble vitamins, vitamin D is not stored in the liver. The main storage sites are fatty tissue and muscle.
It is the vitamin that governs calcium and bones.
It is therefore very important. If the parrot lacks vitamin D, it cannot synthesize its calcium. So there, big problem. This vitamin also regulates the metabolism of phosphorus. Absorption takes place by sunlight (UV). If the bird lacks sunlight, it can be supplied with good UV rays with fluorescent tubes like “Vitalite, Verilux Tru-bloom, or others”. Ask your local pet store. There is no point in placing the parrot in front of a window on a sunny day. The glass absorbs too many UV rays.
The recommended dose of vitamin D3 in a normal maintenance diet is 1000u.i. / kg.
Deficiency in parrots
Poor calcification of eggs (soft, misshapen), egg retention, beak deformation, growth retardation, rickets, bone deformity, lack of coordination, dizziness, very dull plumage, nervousness, gout, liver disease, and kidneys.
Overdose
Vitamin D poisoning causes mineralization in soft tissues (calcification), especially the kidneys and digestive tract. Anorexia, lameness, lethargy, diarrhea, reduced reproductive performance are other symptoms seen in parrots who receive too much vitamin D in their diet.
Vitamin D3 (International unit / 100 g.)
Fish oil
Sardines in oil 10,000
Egg yolk 1,380
Fish liver 265
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is a group of chemical compounds called Tocopherols. Vitamin E acts as an antioxidant in the tissues and cells of the body, helps infertility, maintains muscles and nerves.
Deficiency in parrots
Infertility, lack of coordination, convulsions, weakness, paralysis, little resistance to infections, gastrointestinal and cardiovascular problems, muscle wasting, hemorrhages.
Parrot Vitamins
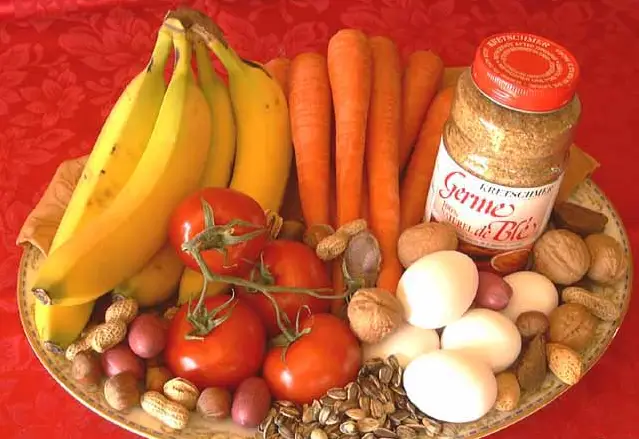

Vitamin E
Vitamin E is found in Alfalfa
wheat germ Safflower oil Eggs Nuts, almonds, hazelnuts, sunflowers Soy Bananas, carrots, tomatoes
Vitamin K
Vitamin K, phytomenadione, consists of 3 similar chemical compounds.
K1: is present in plants.
K2: is produced by the bacterial synthesis in the intestines.
K3: menadione is the one most often present in vitamin supplements.
This vitamin helps the blood to clot.
Deficiency in parrots
Anemia, the tendency to hemorrhages.
Vitamin K is found in
Green leafy vegetables
Fruits
Vegetable oils
Water-soluble vitamins (water-soluble)
The body of parrots does not store these vitamins. When birds ingest water-soluble vitamins, the body absorbs some of them and eliminates the excess through bodily fluids.
Vitamin B1
Thiamine
Regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates (sugars), lipids (fats), and amino acids. These are involved in the production of proteins.
Deficiency in perroquety
Growth retardation, convulsions, weakness, paralysis, diarrhea, degeneration of heart muscle and nerves, depression, circulatory, eye, and mental disorders.
Vitamin B1 is found in whole
grains
Brazil nuts
Brewer’s yeast
Egg yolk
Vitamin B2
Riboflavin
Vitamin for energy and muscle cramps.
Regulates hormonal metabolism, digestion, iron fixation in the blood.
Deficiency in parrots
Depigmentation of feathers in baby cockatiels, reduced egg production, lack of coordination, weakness, paralysis, dull plumage, loose feathers, dizziness, dizziness.
Vitamin B2 is found in
Brewer’s yeast
Eggs
Cheese
Almonds
Beef liver
Vitamin B3
Niacin
Regulates the digestive system, skin health, and blood circulation.
Helps reduce cholesterol levels.
Deficiency in parrots
Growth retardation, dermatosis, dull plumage, inflammation of the oral cavity, digestive problems, fatigue, nervousness, anxiety, intolerance to the sun.
Vitamin B3 is found in
Brewer’s yeast
Tofu
Calf liver
Lean meats
Fish
Cereals
Soy
Vitamin B5
Pantothenic acid
Vitamin B5 deficiency is very rare because it is present in all living cells and in all foods. On the other hand, absorption can be disturbed by parasites or an infection of the digestive tract.
- It is essential for growth.
- Reduces the side effects of antibiotics.
Deficiency in parrots
Growth retardation, skin damage, dull plumage, liver problems, degeneration of the spine.
Vitamin B5 is found in
Salmon
Brewer’s yeast
Cooked mushrooms
Vitamin B6
Pyridoxine
Participates in the regulation of protein metabolism. Binds iron in the blood.
Deficiency in parrots
Growth retardation, convulsions, anemia, anorexia, weight loss, arthritis.
Parrot Vitamins
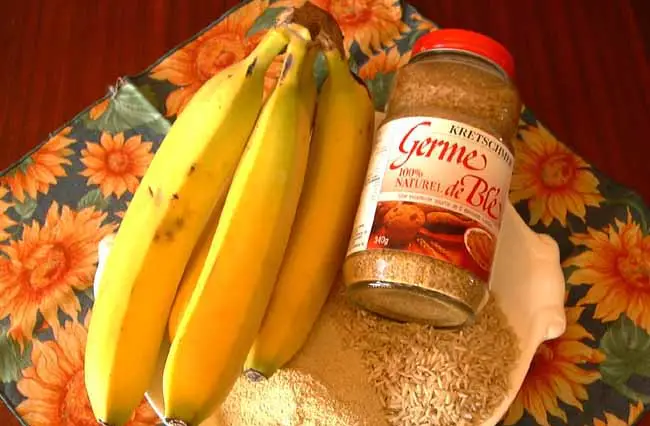

Vitamin B6
Vitamin B6 is found in
Brewer’s yeast
Liver
Bananas
Grain sprouts Brown
rice
Vitamin B9
Folic acid
Analgesic properties, protein metabolism, and formation of red blood cells.
Plays a role in growth and reproduction.
Deficiency in parrots
Prevents reproduction, stunted growth, dull plumage, anemia, digestive disorders.
Vitamin B9 is found in Brewer’s
yeast
Green
salad Dried dates
Tuna, salmon
Oil
Soy flour
Vitamin B12
Cyanocobalamin
It is the only vitamin to contain an inorganic element: cobalt.
Vitamin B12 intake should be increased during reproductive times and in cases of hyperthyroidism.
If the bird’s diet is low in calcium, vitamin B12 absorption will be more difficult. It is not uncommon to see a vitamin B12 deficiency in parrots.
Deficiency in parrots
Difficult reproduction, growth retardation, bone deformity, dull plumage, anemia, hinders red blood cell production, nervous system damage, weakness.
Vitamin B12 is found in
Beef liver
Tuna
Beef
Eggs
Corn
Vitamin B17
Biotin
Regulates the synthesis of fatty acids, amino acids, and hemoglobin.
Allows the use of vitamin B because biotin is produced by bacteria in the intestine.
The administration of antibiotics, particularly sulfa drugs, can create a vitamin B17 deficiency.
Deficiency in parrots
Difficult reproduction, growth retardation, bone deformation, dizziness, loss of balance, skin problems, nasal and eye discharge, limb deformity, fatty liver.
Vitamin B17 is found in
Egg yolk Whole grain
rice
Brewer’s yeast Whole
grains
Choline
THE liver vitamin. In combination with methionine, it can help prevent fatty liver problems.
Deficiency in parrots
Growth retardation, dull plumage, stretching of tendons, fatty liver, anorexia, hypertension.
Choline is found in
Soy
Egg yolk
Lecithin Brewer’s
yeast
Fish
Vitamin C
Ascorbic Acid
Vitamin C is naturally synthesized in the liver of some birds during glucose conversion. The addition of this vitamin in the bird’s diet is not necessary according to some experts.
Others claim it is essential for birds, especially during breeding, growth, disease, and times of stress. If in doubt, it is better to provide it to your parrot.
Deficiency in parrots
Weakness, reduced immunity, the tendency to hemorrhages, bruises.
Parrot Vitamins
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is found in
Fruits
Oranges
Lemons
Blackcurrant
Parsley
Vegetables
All about vitamin deficiency in birds
SOURCE:Denny the Budgie




















