
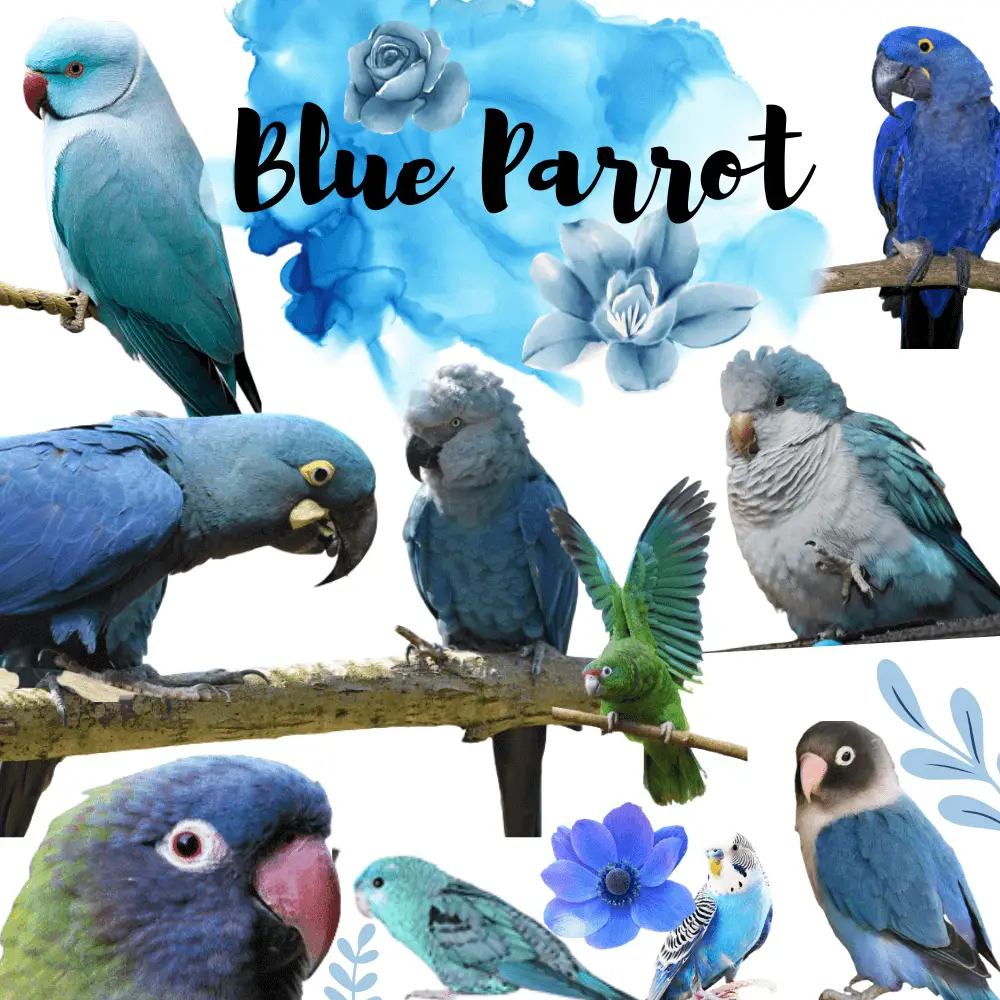
List of Blue Parrots species to keep as pets, Although green is a dominant color in many parrots, there are still several pet birds with beautiful blue feathers.
Blue parrot species range from small to very large and come in powdery light blue and deep indigo. Some of these birds simply have flashy blue markings while others are mostly blue. Here are eight species of blue parrots that you will often find as pet birds.
Blue Parrot Species
Il existe de très nombreuses races de perroquets. Chaque espèce ou race possède ses propres spécificités et caractéristiques
Hyacinth Macaw

Blue-and-Gold Macaw

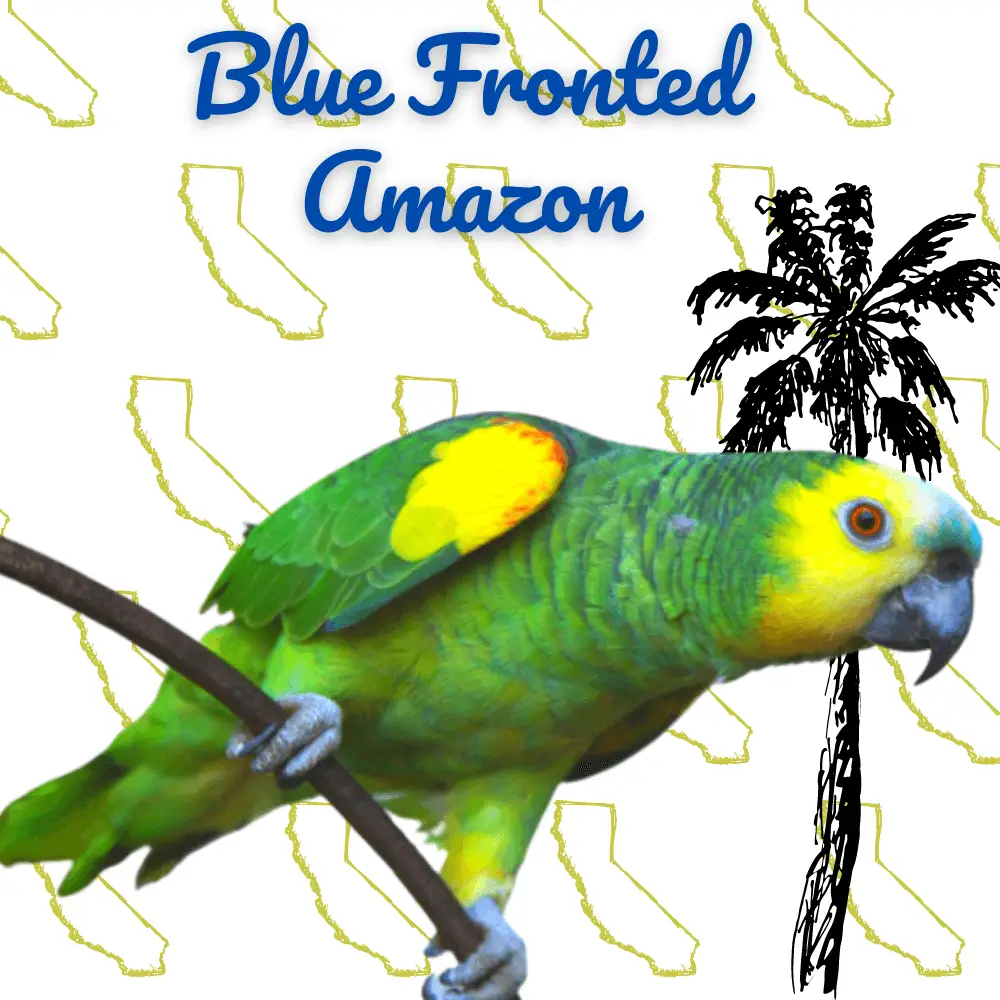
Blue Fronted Amazon

Blue Indian Ringneck Parakeet

Lear’s Macaw (Indigo Macaw)

Bleu Pacific Parrotlet

Blue Quaker Parrot

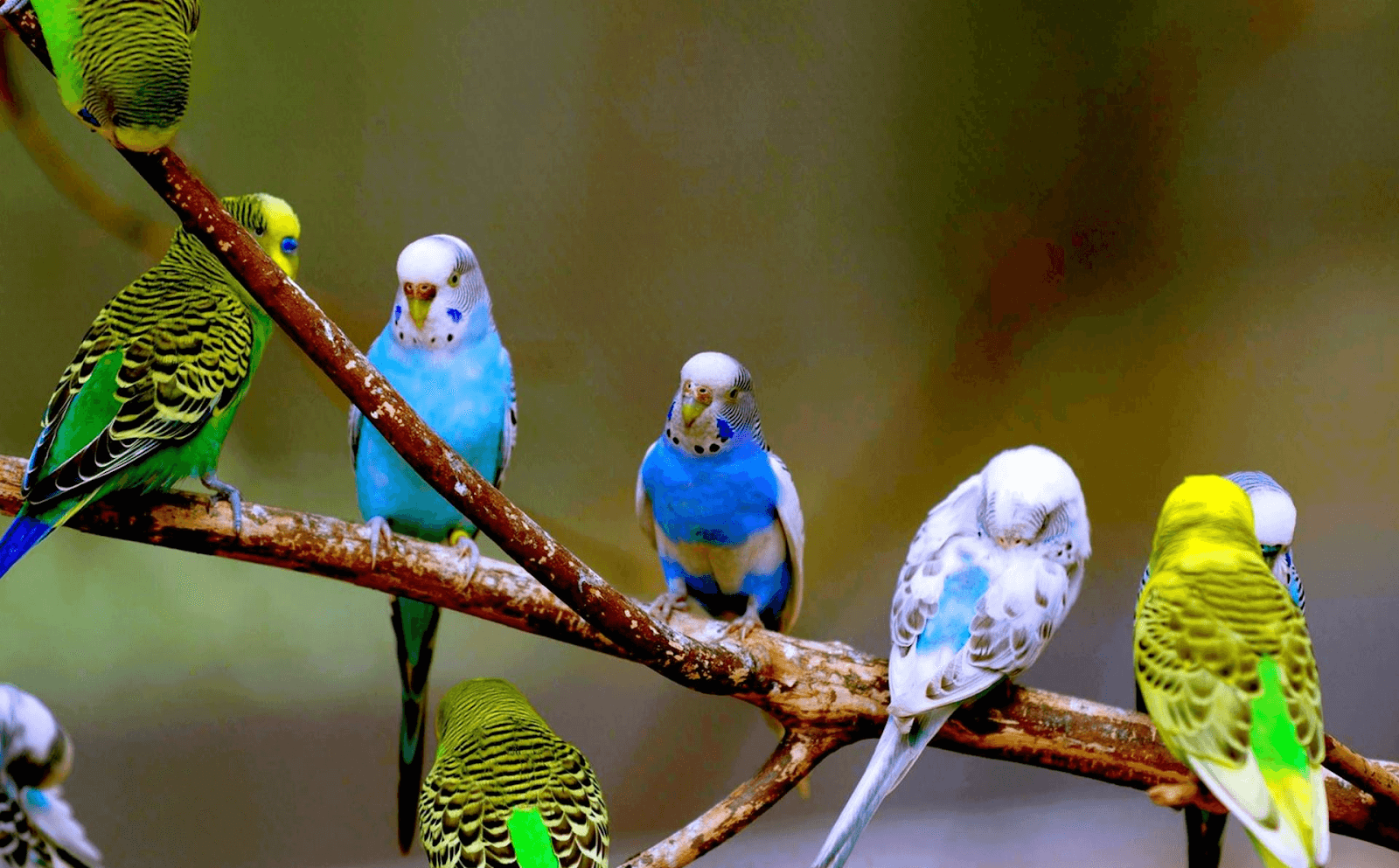
Bleu Budgerigar
Blue-Headed Pionus

Identification: Blue-headed Pione (Pionus menstruus) is a bird that belongs to the family Psittacidae and the order Psittaciformes.
Blue-Crowned Conure
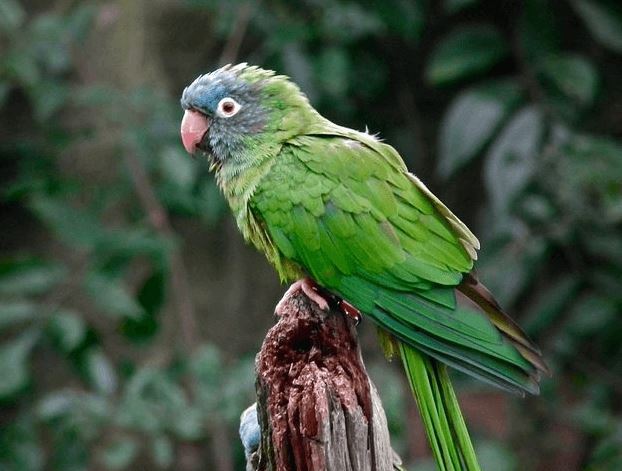

The Blue-headed Conure (Thectocercus acuticaudatus) is a parakeet in the order Psittaciformes and family Psittacidae.
Blue-throated macaw
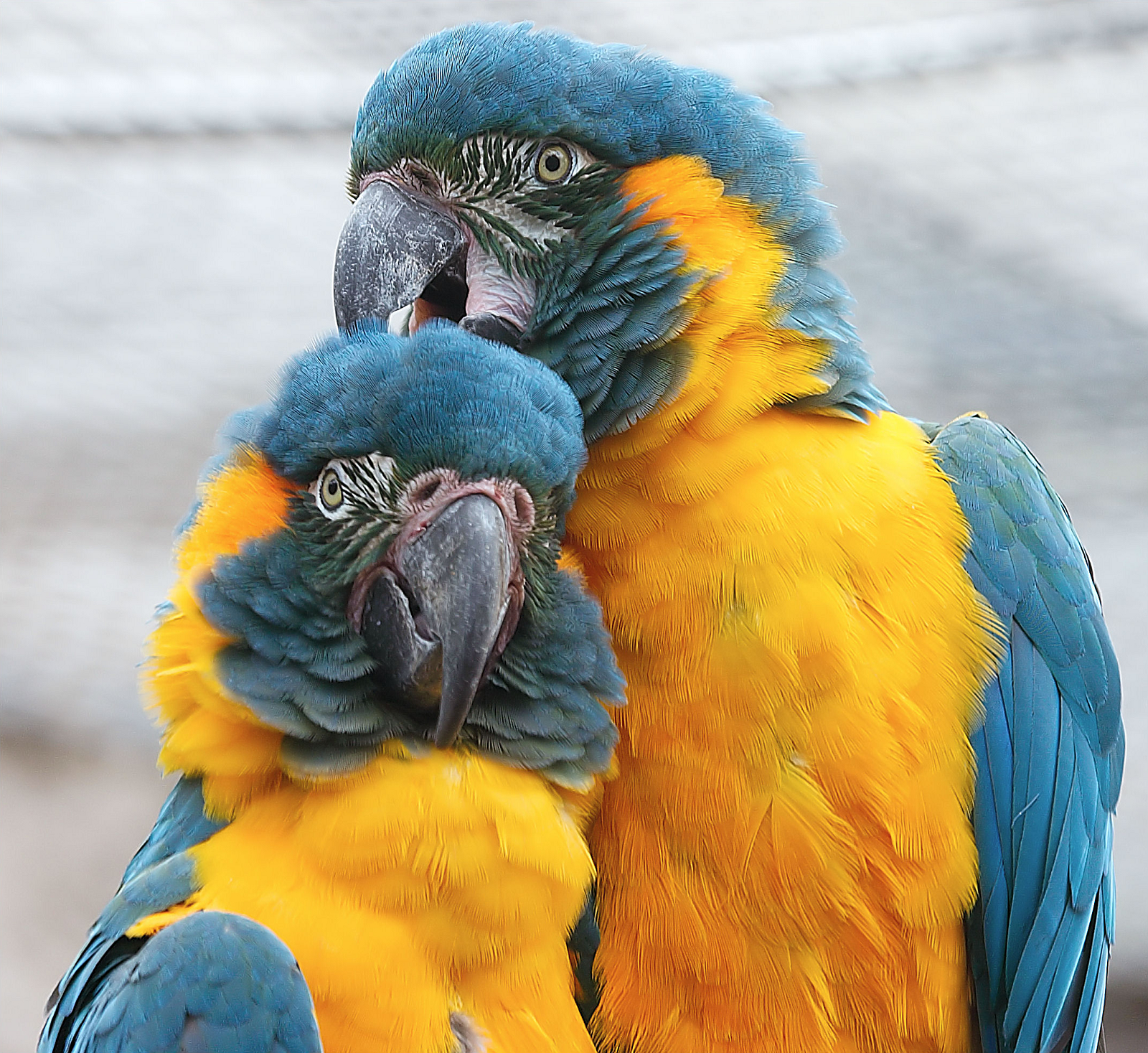

The Blue-throated macaw, also known as the Caninde macaw or Wagler’s macaw, is a macaw endemic to a small area of north-central Bolivia, known as Los Llanos de Moxos.
Blue-headed Racquet-tail
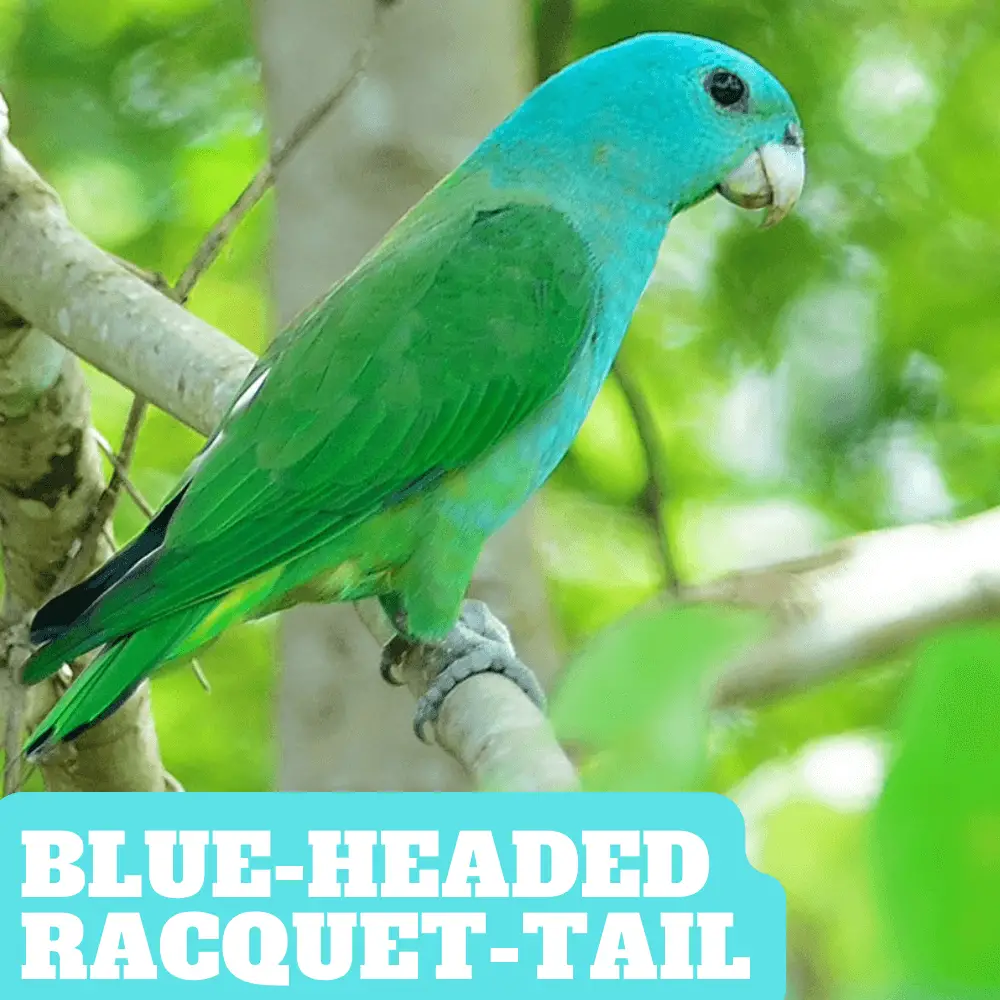

Blue-headed Racquet-tail 27 cm. Pale greyish-yellow bill; entire head and nape light blue extending onto the breast
Blue-crowned Racquet tail
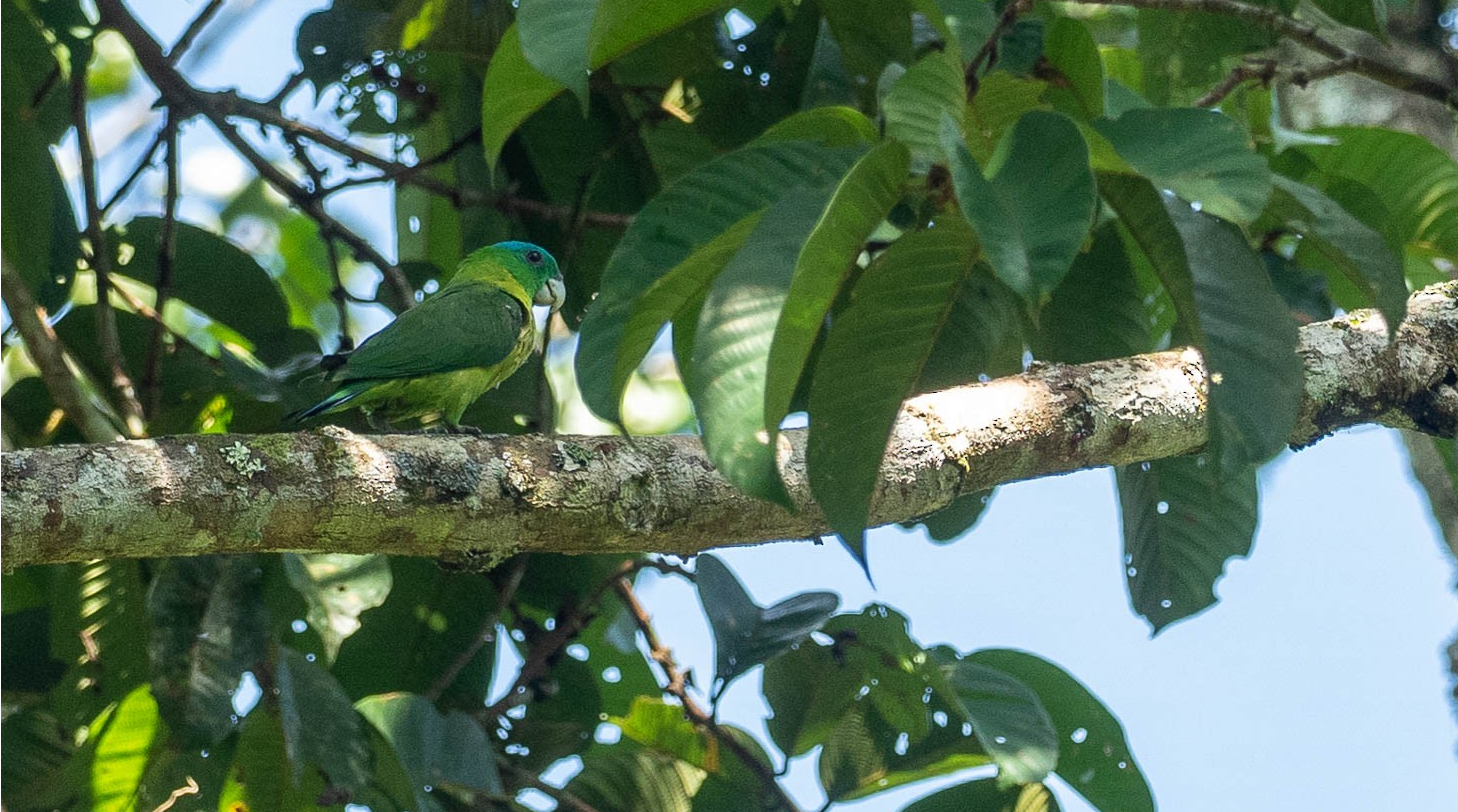

Blue-crowned Racquet tail(Prioniturus discurus) 27 cm; 86–176 g. Crown to hindneck pale blue
Blue-winged Racquet-tail Parrot

Blue-winged Racquet-tail Parrot 28–30 cm, plus racquets of 5–6 cm
Blue rumped Parrot
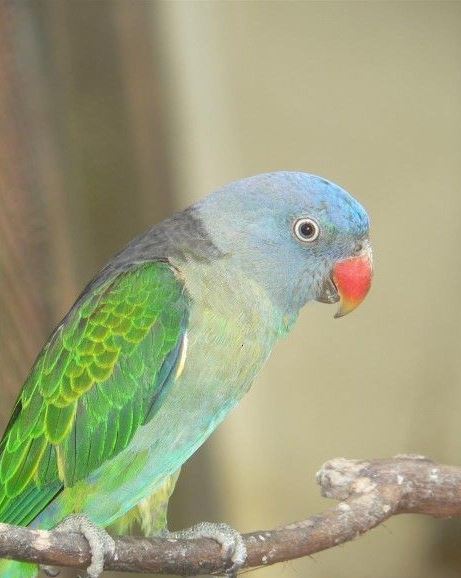

Blue-rumped Parrot 18–19·5 cm. Upper mandible red (lower duller); head lavender-blue
Blue-winged Parrot
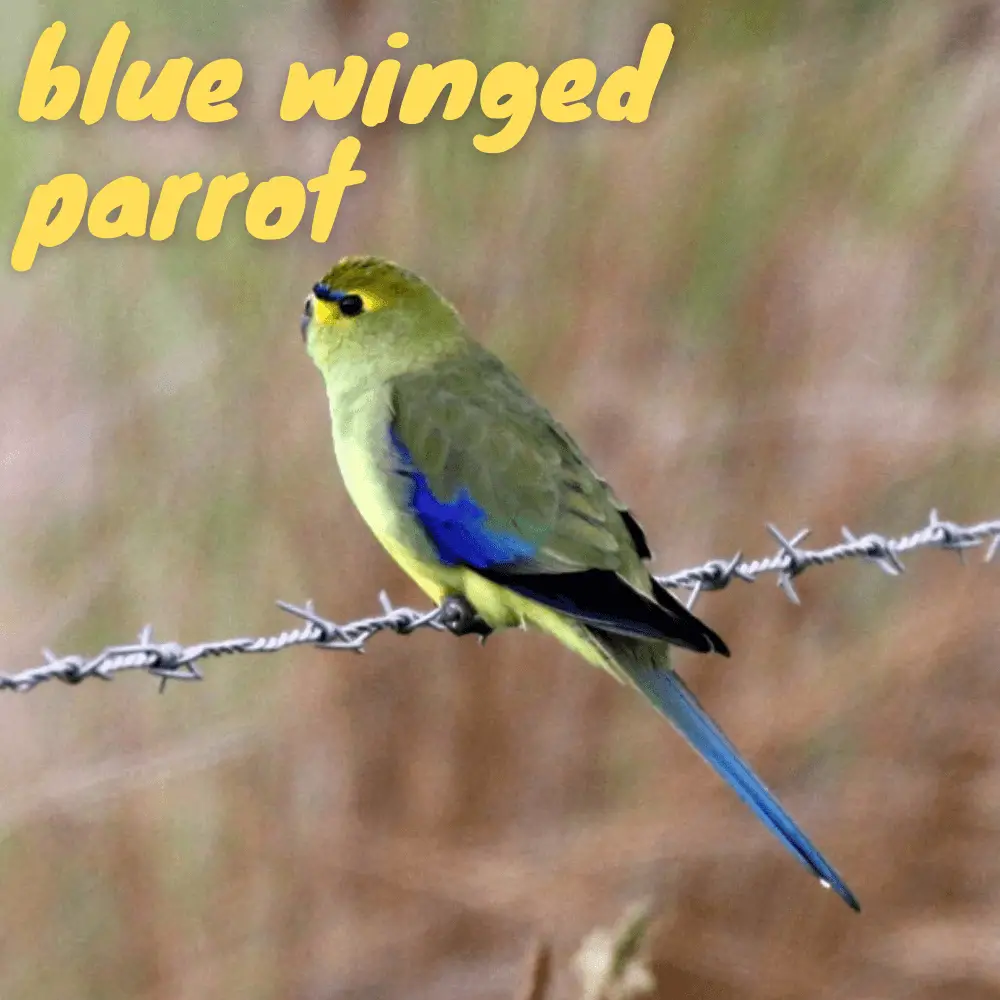

Blue-winged Parrot 20–21 cm; 44–61 g. The area between the eye and bill, and postocular mark, yellow; dark blue line across the forehead to the front of the eye,
Eastern bluebonnet
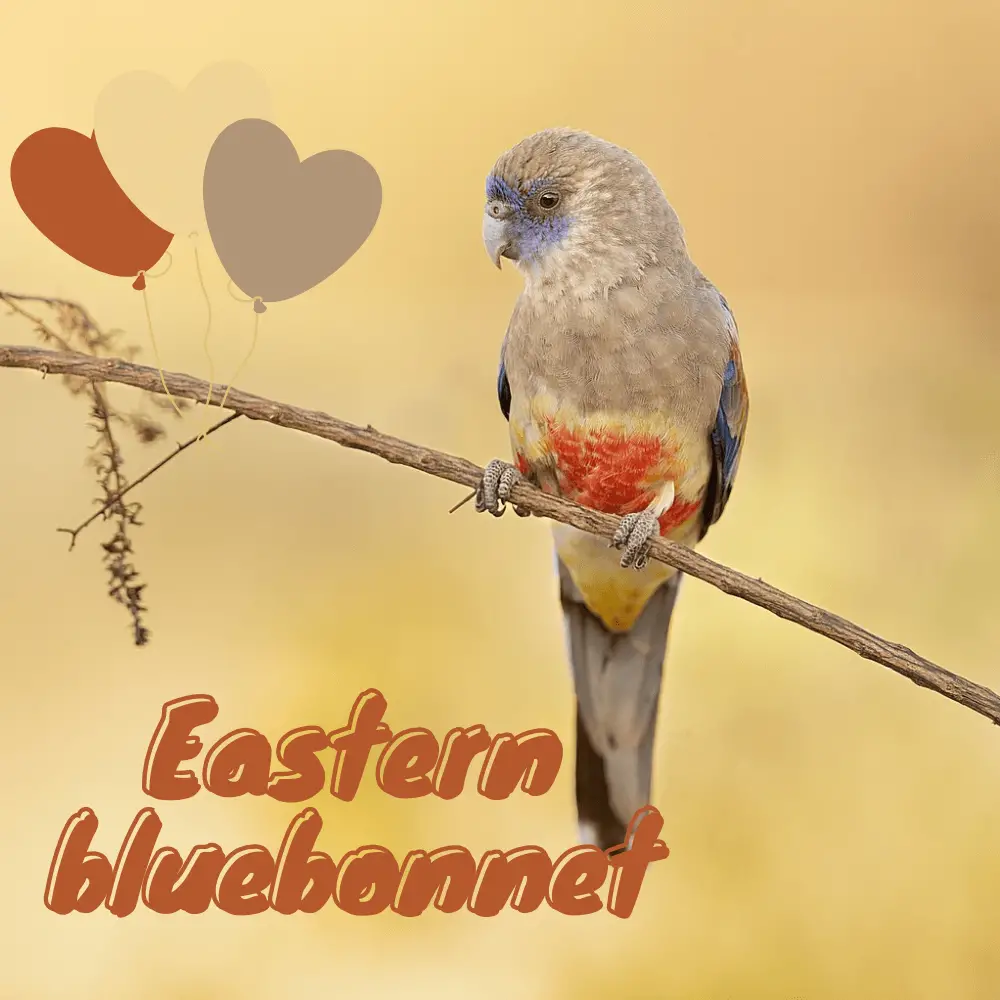

Eastern bluebonnet or Greater Bluebonnet 28 cm; 74–105 g. Forehead, lores, and face purplish-blue
Blue Lorikeet

Blue Lorikeet 18 cm; 31–34 g. Orange bill and legs, white from the line through the eye to ear-coverts down to the breast, otherwise deep purplish-blue
Blue-crowned Lorikeet

Blue-crowned Lorikeet 19 cm; 47–52 g. Orange bill, grass-green forehead backed by pale bright purplish-blue
Blue-crowned Hanging Parrot

Blue-crowned Hanging Parrot 12–14·5 cm; 22–35 g. Bright emerald, more yellowish on underparts; bill black; middle of crown blackish blue
Blue-cheeked Amazon
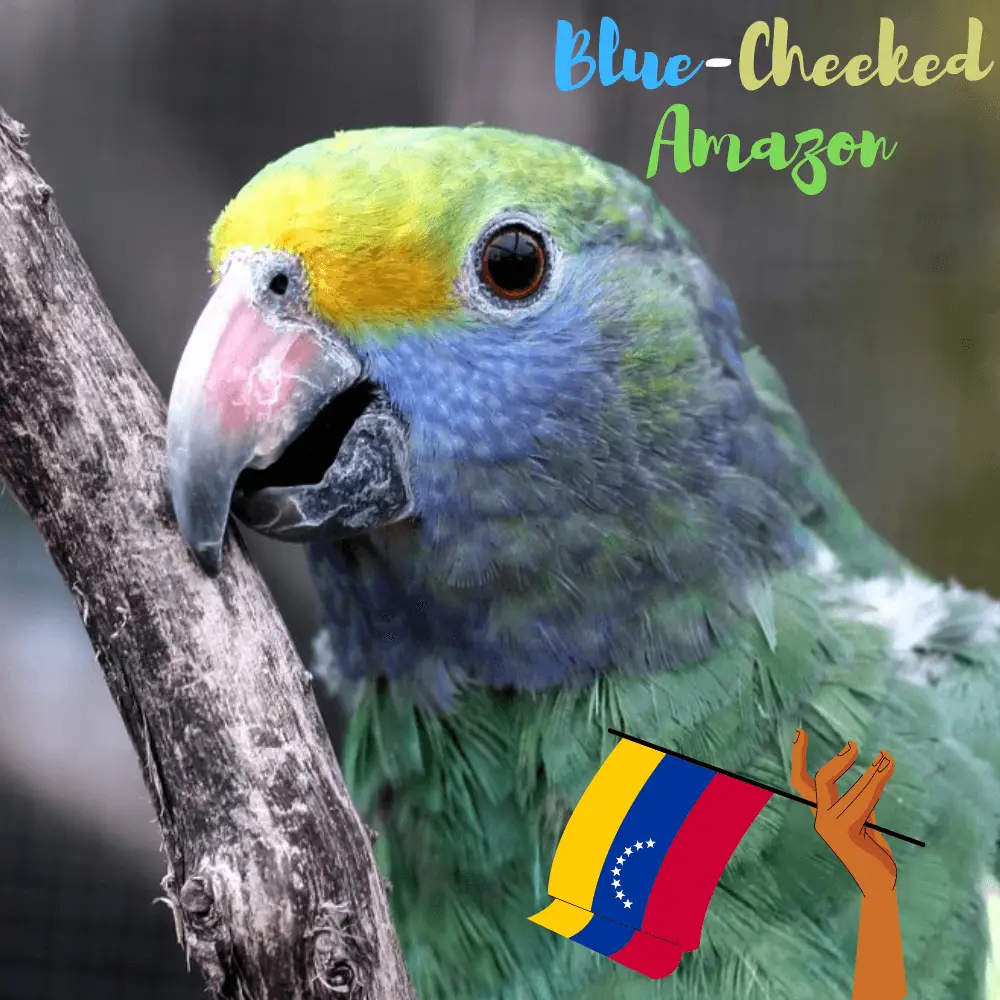

The Dufresne’s Amazon or Blue-cheeked amazon also known as a blue-cheeked parrot (Amazona dufresniana)
Blue-naped Parrot
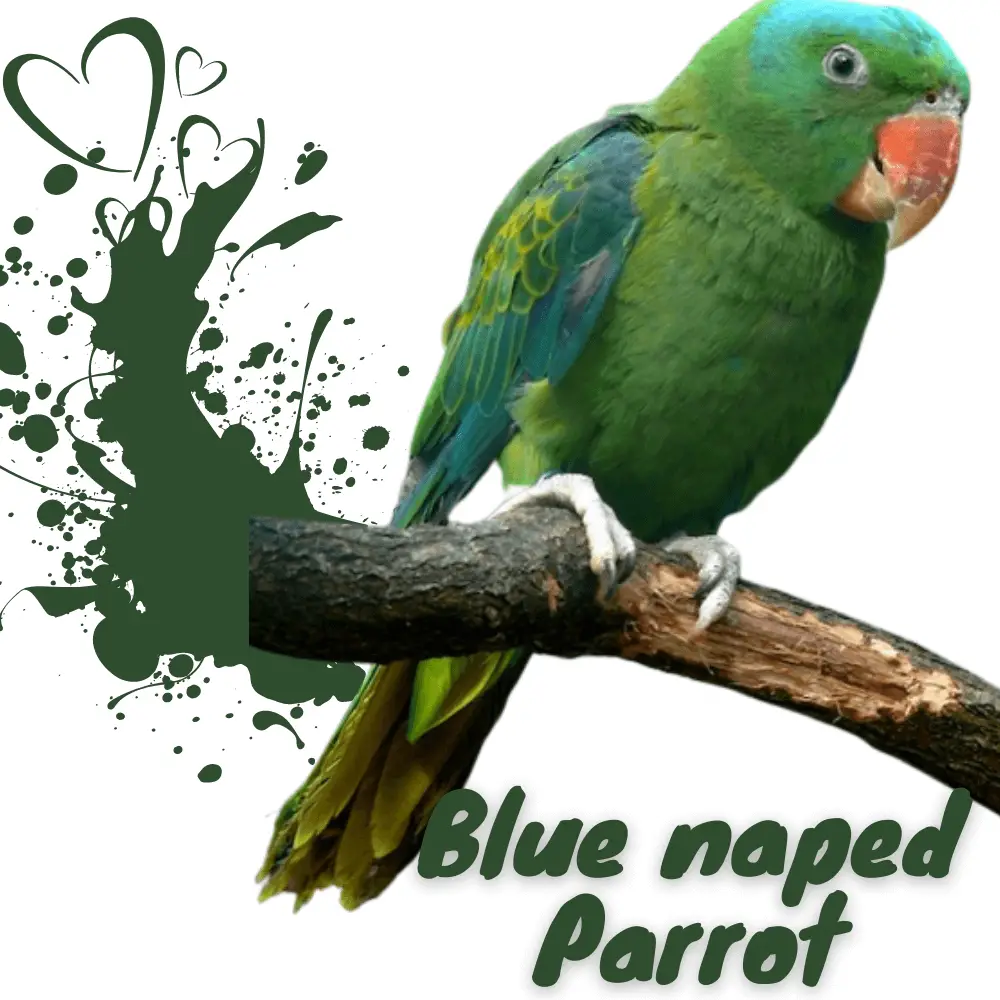

Blue-naped Parrot 31 cm; 148–231 g. Green, brighter on head and rump; bill red; mid-crown to nape pale blue; back suffused blue
Naretha Bluebonnet

Naretha Bluebonnet 28 cm; 74–105 g. Forehead, lores, and face purplish-blue, head, breast, mantle, back,
Where Do Blue Parrots Come From?
Blue parrots live in hot, tropical climates. Australia, Indonesia, the Philippines, and New Guinea host blue parrots, though the catcalls are most crowded in South and Central American homes, especially in Brazil. The Blue- and-unheroic Macaw can be set up in Florida.
The rainforest home of numerous blue parrots is being devastated. The Glaucous Macaw, for illustration, is critically exposed – supposed defunct by some experts – as its terrain in Argentina, Bolivia, Uruguay, Brazil, and Paraguay was destroyed and inhabited by humans.
How Long Do Blue Parrots Live?
| Blue-and-Gold Macaw | 70 or 80 years |
| Blue-crowned Conure | 30 years |
| Blue-Headed Pionus | 40 years |
| Budgerigar | 8 years to 20 years |
| Hyacinth Macaw | 60 years |
| Indian Ringneck Parakeet | 20 years 30 years |
| Lear’s Macaw | 30 years to 50 years |
| Pacific Parrotlet | 10 years to 25 years |
| Quaker Parrot | 20 years to 30 years |
| White-capped Pionus | 30 years, possibly longer |
Why are parrots colored?
The feathers of parrots protect them from moisture, cold, heat, and dust, and allow them to fly. However, they are fragile and susceptible to attacks by bacteria that break them down. Parrots defend themselves in an amazing way: with their colors! Indeed, unlike other birds, they themselves produce red pigments and do not get them in their food. Their red dyes prevent bacterial attacks, presumably because their molecules are larger and have stronger bonds, thus offering more resistance.
- Red pigments serve as protection.
- Parrots almost always live in large groups.
- The smallest species is the microsite, New Guinea pygmy, an 8 cm parakeet.
- Most parrots are able to fly fast and far.
- In the mating season, parrots parade in their sumptuous plumage.
- The hyacinth macaw, which lives in the tropical forests of South America, is the largest parrot (1 m from beak to tail).
- Couples often form for life.

What Makes Parrots Blue
Blue parrots get their color from keratin, which is the protein set up in mortal hair and nails. Keratin sits within the feathers, and the three primary colors set up in feathers blue, unheroic, and red reply to the sun.
Suppose a pantomimist Shastri-color feathers. Keratin forces red and unheroic tones to cancel each other out, and this means the blue feathers come dominant and unmistakable. From deep to pale, the shade of blue depends on how important keratin remains in the pantomimist’s feathers.
How Much Do Blue Parrots Cost?
| Blue-and-Gold Macaw | $1,500 |
| Blue-crowned Conure | $1,000 to $2,000 |
| Blue-Headed Pionus | $1,000 or more |
| Budgerigar | $40 |
| Hyacinth Macaw | $5,000 to $10,000 |
| Indian Ringneck Parakeet | $1,500 or more |
| Lear’s Macaw | $3,000 |
| Pacific Parrotlet | $300 |
| Quaker Parrot | $250 |
| White-capped Pionus | $500 to $1,000 |




















